Cheese is a beloved food around the world, and the United States is no exception. With a rich history of cheese production, the country has become a major player in the global cheese market.
In this article, we will explore the process of cheese production in the United States, the different types of cheese produced, and the impact of the industry on the economy and environment.
The Process of Cheese Production
Cheese production involves several key steps, each of which contributes to the final product’s flavor, texture, and quality. Let’s take a closer look at the process:
Milk Collection and Quality Control
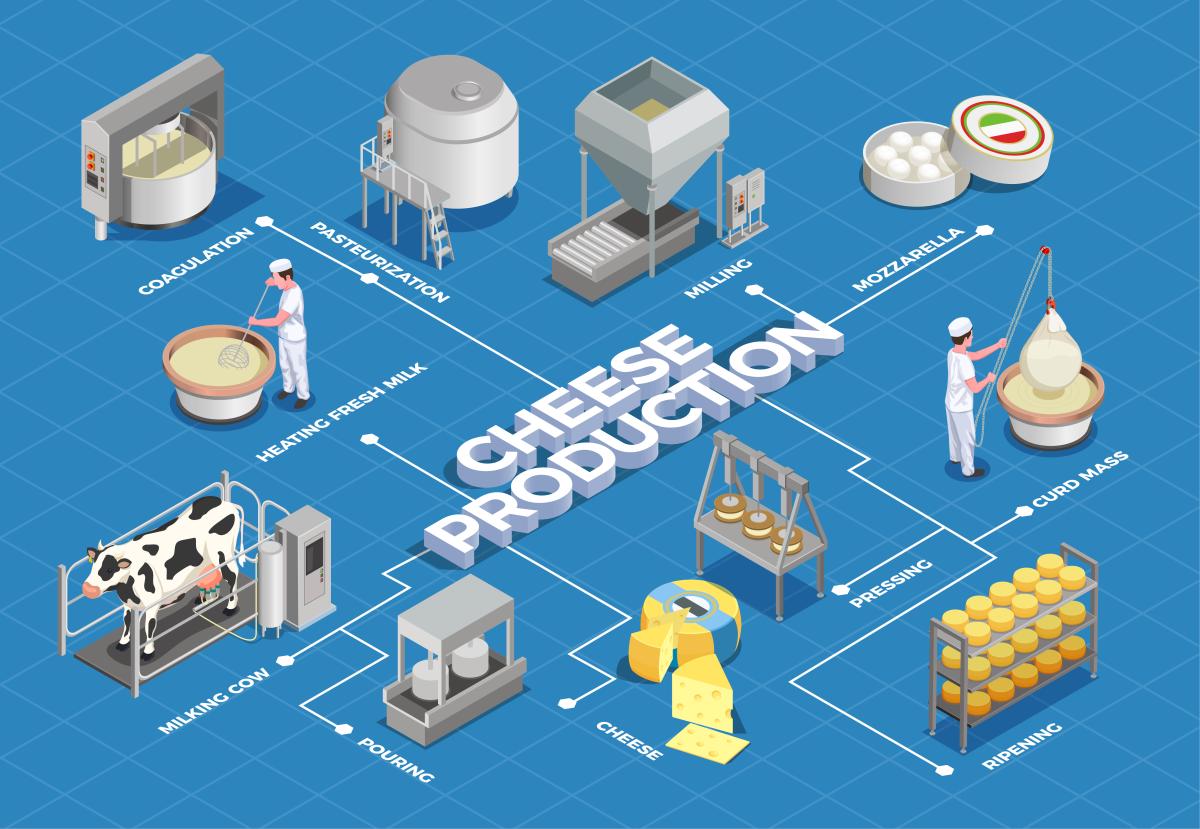
The first step in cheese production is milk collection. Dairy farmers across the United States supply milk to cheese manufacturers. The quality of the milk is crucial, as it directly affects the taste and quality of the cheese. To ensure high standards, milk undergoes rigorous testing for factors such as bacterial count, somatic cell count, and fat content.
Curd Formation
Once the milk passes quality control, it is heated and mixed with starter cultures and rennet. Starter cultures are responsible for acidifying the milk, while rennet helps coagulate it. The coagulated milk forms curds, which are then cut into smaller pieces to release whey.
Whey Separation
After curd formation, the whey is separated from the curds. This can be done through various methods, such as draining or pressing. The whey, which contains water, lactose, and some proteins, is often used in other food products or as animal feed.
Cheese Molding
The separated curds are then shaped and pressed into cheese molds. Pressed into cheese molds refers to the process of shaping and compacting curdled milk into a specific form using a cheese mold. This technique is crucial in the production of various types of cheeses. Once the curds have been formed and drained, they are carefully placed into the molds, which can be made of various materials such as wood, plastic, or metal.
The pressing stage is essential as it helps remove additional whey from the curds and encourages the consolidation of the cheese. This process results in the desired texture and density of the final product. The pressure applied during pressing also contributes to the development of the cheese’s characteristic shape, rind, and flavor.
Different cheeses require varying degrees of pressure and duration of pressing. Soft cheeses, like Camembert or Brie, are lightly pressed to maintain their creaminess. In contrast, semi-hard and hard cheeses, such as Cheddar or Parmesan, are subjected to more substantial pressure for an extended period. The pressing time and weight can be adjusted to achieve the desired moisture content, texture, and taste.
Once the curds have been pressed into the molds, they are often flipped or turned regularly to ensure even distribution of pressure and to prevent any imbalances. This rotation allows for uniform consolidation and prevents any uneven shaping or air pockets from forming within the cheese.
Cheese Maturation
During this stage, the cheese develops its unique flavor and texture. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and aging time play a crucial role in determining the final characteristics of the cheese.
Packaging and Distribution
Once the cheese has matured, it is packaged and prepared for distribution. Cheese can be sold in various forms, such as blocks, slices, or shredded. It is then distributed to retailers, restaurants, and other food establishments across the country.
Types of Cheese Produced in the United States
The United States produces a wide variety of cheeses, each with its own distinct characteristics and flavors. Here are some of the most popular types:
- Cheddar: Cheddar is one of the most widely consumed cheeses in the United States. It is known for its sharp, tangy flavor and smooth texture.
- Mozzarella: Mozzarella is a versatile cheese commonly used in pizzas and pasta dishes. It has a mild, creamy taste and a stretchy texture when melted.
- Swiss: Swiss cheese is characterized by its distinctive holes and nutty flavor. It is often used in sandwiches and fondue.
- Blue: Blue cheese is known for its pungent aroma and blue veins running through it. It has a strong, tangy flavor and is often crumbled over salads or used in dressings.
- Monterey Jack: Monterey Jack is a semi-hard cheese with a mild, buttery taste. It melts well, making it a popular choice for grilled cheese sandwiches and quesadillas.
The Impact of Cheese Production on the Economy and Environment
The cheese production industry in the United States has a significant impact on both the economy and the environment. Let’s examine these impacts in more detail:
Economic Impact
Cheese production contributes significantly to the U.S. economy. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the cheese industry generated over $45 billion in economic output in 2020. It also provides employment opportunities for thousands of people, from dairy farmers to cheese manufacturers and distributors.
Furthermore, the export of American cheese contributes to the country’s trade balance. The United States is one of the largest cheese exporters globally, with countries such as Mexico, Canada, and Japan being major importers of American cheese.
Environmental Impact
While cheese production has economic benefits, it also has environmental implications. One of the main concerns is the carbon footprint associated with dairy farming and cheese manufacturing. The dairy industry is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily through methane released by cows and energy consumption during the production process.
Efforts are being made to reduce the environmental impact of cheese production. Some dairy farms are adopting sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources and implementing manure management systems to reduce methane emissions. Additionally, cheese manufacturers are exploring more energy-efficient production methods and investing in waste management systems.
Get the news first!
Summary: The Rich World of Cheese Production in the United States
Cheese production in the United States is a complex and thriving industry. From the collection of high-quality milk to the maturation of cheese, each step in the process contributes to the creation of unique and delicious cheeses. The industry has a significant impact on the economy, generating billions of dollars in revenue and providing employment opportunities. However, it also faces challenges in terms of its environmental impact, particularly in relation to greenhouse gas emissions. By adopting sustainable practices and investing in innovative solutions, the cheese production industry can continue to thrive while minimizing its ecological footprint.
Key Takeaways
- Cheese production in the United States involves several key steps, including milk collection, curd formation, whey separation, cheese maturation, and packaging.
- Popular types of cheese produced in the United States include cheddar, mozzarella, Swiss, blue, and Monterey Jack.
- The cheese production industry has a significant economic impact, contributing billions of dollars to the U.S. economy and providing employment opportunities.
- However, cheese production also has environmental implications, particularly in terms of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Efforts are being made to reduce the environmental impact of cheese production through sustainable practices and innovative solutions.
Make Cheese!